
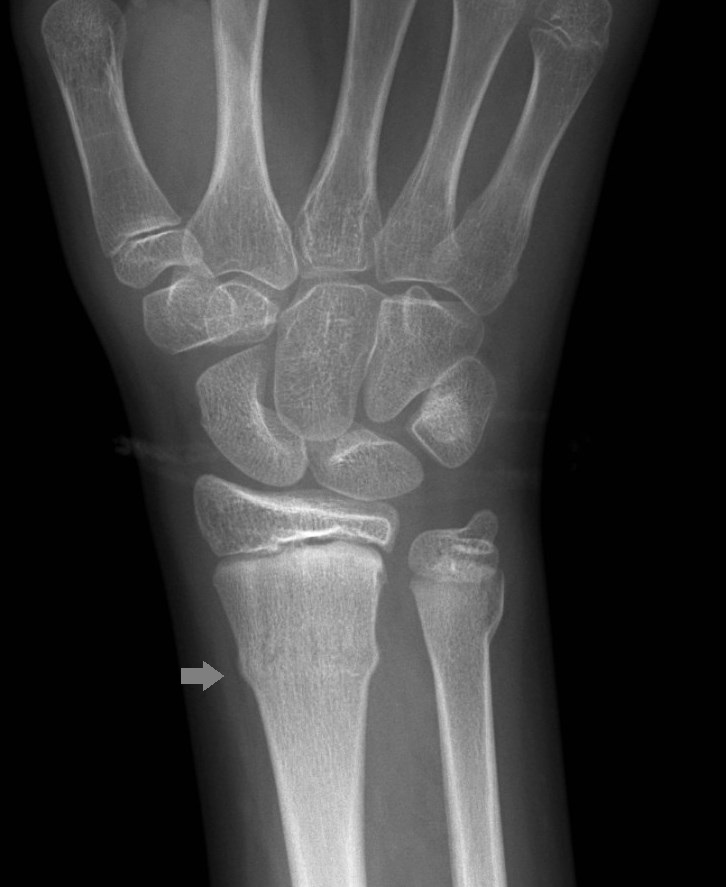
A torus is the convex portion of the upper part of the base of a Greek column and resembles the appearance of the cortical buckling seen in the "column" of bone which has been fractured in the pattern discussed in this article. A buckle fracture is a unique type of fracture that most often occurs in children. Ésta es una fractura estable y los pedazos rotos del hueso no se han separado (desplazado). A torus fracture ( buckle fracture) is an incomplete fracture creating a buckle of the cortex, always at the concave side. La capa más superior del hueso en un lado del hueso es comprimida, causando que el otro lado se doble hacia afuera del cartílago de crecimiento.
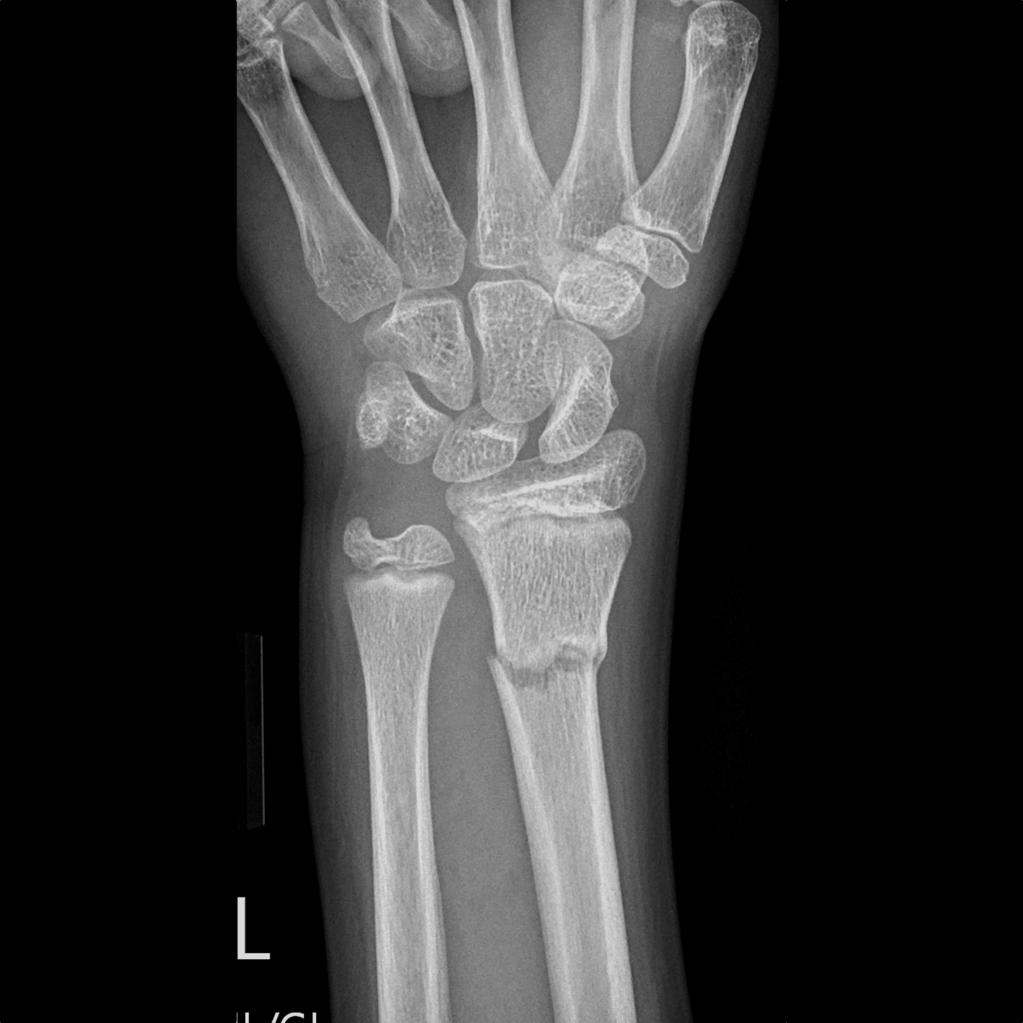
They are usually seen in children, frequently involving the distal radial metaphysis. They result from trabecular compression due to an axial loading force along the long axis of the bone. The term torus is the Latin word meaning protuberance. También se conoce como 'fractura en rodete'. Torus fractures, also known as buckle fractures, are incomplete fractures of the shaft of a long bone that is characterised by bulging of the cortex. Sometimes a cast may be applied, but often a splint is all that is required with a period of rest and immobilisation.
#Torus fracture professional
Please consult with your doctor or other health professional to. They are self-limiting and typically do not require operative intervention, although a manipulation may be required if the angulation is severe. Disclaimer: This fact sheet is for education purposes only. in some cases, angulation is the only diagnostic clue.subtle deformity or buckle of the cortex may be evident.This most commonly occurs at the distal radius or tibia following a fall on an outstretched arm the force is transmitted from carpus to the distal radius and the point of least resistance fractures, usually the dorsal cortex of the distal radius. Torus fractures (also called buckle fractures) of the wrist are the most common type of broken bone in. This injury is also called an incomplete fracture for this reason. Because of a child’s softer bones, one side of the bone might buckle or bend without any break in the other side. Background: In a torus fracture, there is an intact cortex at the side of the fracture which gives more intrinsic stability than in greenstick fractures, where one side of the cortex is disrupted. This is a very common fracture in children. Cortical buckle fractures occur when there is axial loading of a long bone. Torus Fractures: Evidence from the FORCE study. Your child has a broken bone (fracture) in the forearm (radius or ulna bone).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
